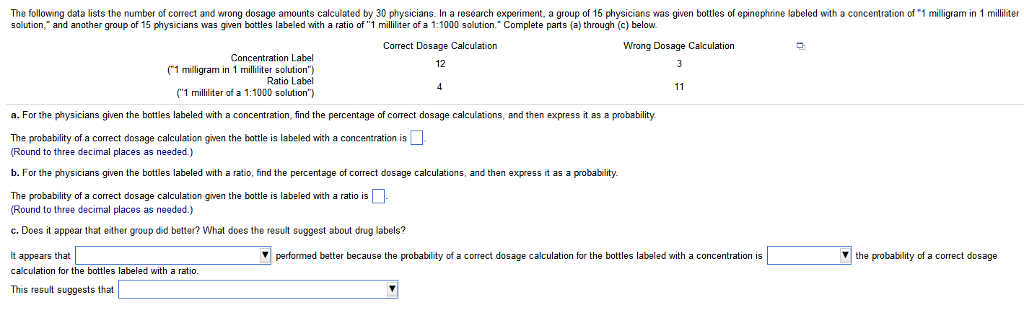
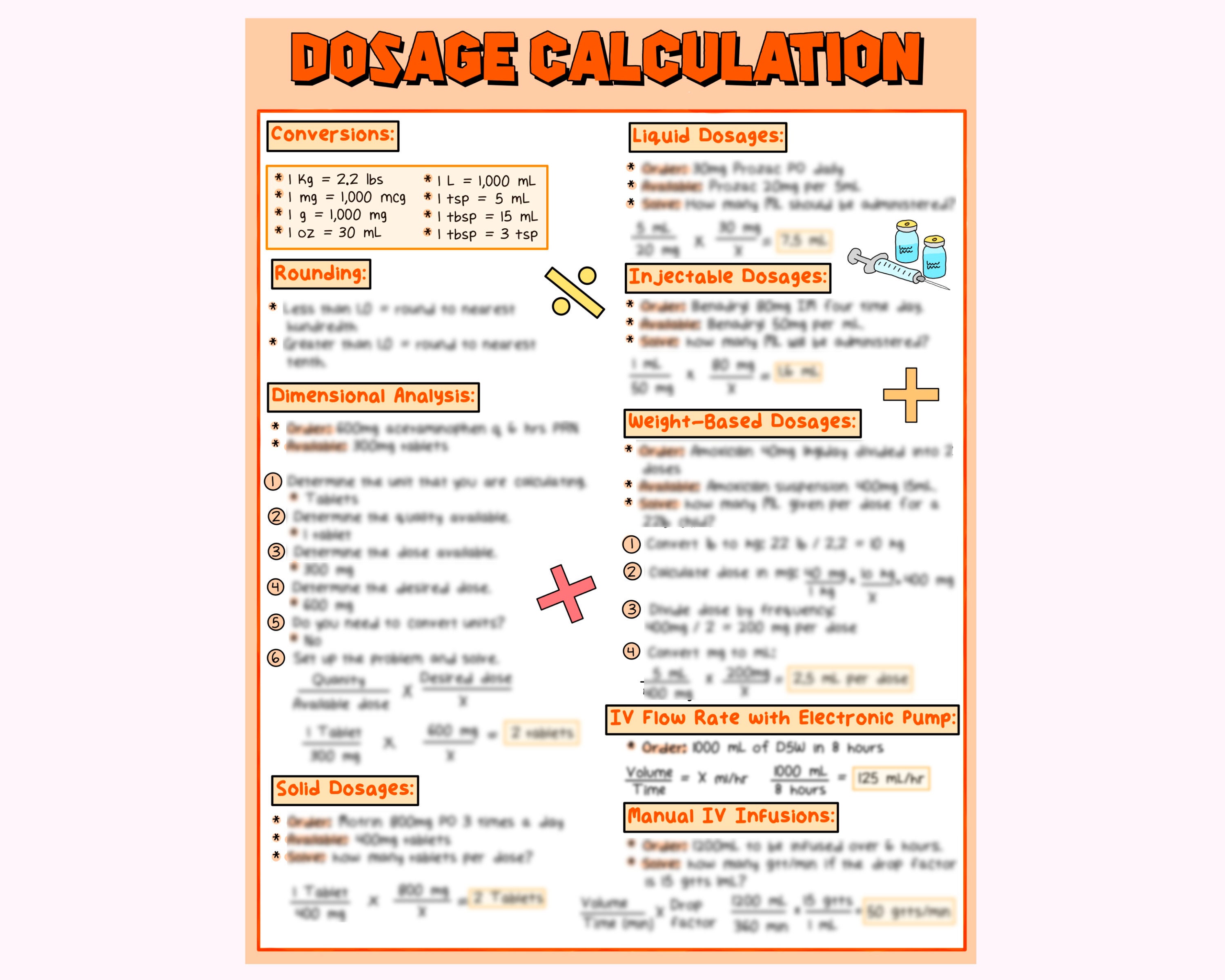
43 dosage calculations with labels
Calculating from the labels | Learning Lab Calculating from the labels | Learning Lab Calculating from the labels This short video is the second of three videos in the Nursing calculations - Finding the volume required section. It explains how to calculate medication dosage from labels using the method of mental calculation and proportinality to get the right dosage for drugs in solution. Dose Calculation Dimensional Analysis Factor-Label Method How many milliliters are needed to arrive at the ordered dose? The desired dose gets placed over 1. Remember, (x mL) = 4 mg/1 x 1 mL/2 mg x (4) (1)/2 x 4/2 x 2/1 = 2 mL, the clinician kept multiplying/dividing until they got the desired amount, 2 mL in this problem example.
Medical Dosage Calculations For Dummies Cheat Sheet Common conversion factors in medical dosage calculations. As a healthcare professional, you have to convert patient weights, fluid volumes, medication weights, and more. Conversion math isn't hard to do as long as you know the basic conversion factors. Here are the most useful ones: Converting lb to kg and kg to lb. lb = kg × 2.2. kg = lb ÷ 2.2

Dosage calculations with labels
Dosage Calculation Resources - Calhoun Community College Session 4 Medication Labels Session 5 Formula Method and Ratio to Proportion.pptx Session 6 Parenteral Dosage Session 7 Reconstitution of Solutions & Enteral Feedings Session 8 Pediatric Problems Session 9 IV Calculations Practice Problems Calculating using Labels with Answers Practice Problems Part 1 with Answers Drug Calculations Practice NCLEX Questions (100+ Items) - Nurseslabs Methods for Drug Dosage Calculations Standard Method The commonly used formula for calculating drug dosages. Where in: D = Desired dose or dose ordered by the primary care provider. H = dose on hand or dose on the label of bottle, vial, ampule. V = vehicle or the form in which the drug comes (i.e., tablet or liquid). STANDARD FORMULA Dosage and Calculations Math Practice - StuDocu Any of the following thr ee methods can be used to perform drug calculations. Pl ease. re view all thre e methods and select the one that works for you. It is important to ... H = dose on container label or d ose on hand . V = form and amou nt in which drug comes (tablet, capsule, liquid) Example: Order-Dilantin 50 mg po TID.
Dosage calculations with labels. Drug Calculations: Continuous IV Drips (mcg/kg/min ... Nov 08, 2021 · Step 3: Alternate labels in numerator and denominator so labels cancel out. We want to get to micrograms and we know 1 milligram (mg) equals 1000 micrograms (mcg). Place this in the equation so that milligram labels will cancel out. Add the prescribed dose 10 mcg/kg/min, placing mcg in the numerator so that it will cancel out. Dosage (Drug) Calculations Nursing Review- COMPREHENSIVE Dosage (Drug) Calculations Nursing Review- COMPREHENSIVE This is a comprehensive dosage calculation review for nursing students. In this review we will start by working basic metric conversions and then progress to solving more complex dosage calculations. You will learn how to work the following drug calculation problems: Conversions Oral Drug Dosage Calculator - Liquid Solution Syrup Step By Step Solution: Step 1: Convert input to common units. D (desired) Dose = 500 milligram = 500 milligram H (have) Dose = 250 milligram = 250 milligram Q (quantity) = 5 milliliter = 5 milliliter Step 2: Solve equation. X (amount) = D (desired) Dose H (have) Dose × Q (quantity) X (amount) = 500 milligram 250 milligram ×5 milliliter Dosage Calculator - How to Calculate Dosage? Dosage calculation formulas If you want to calculate the dose of a medication, you need to use the following equation: Dose = Weight × Dosage Dose = W eight × Dosage Where: Weight — Patient's weight, expressed in kg or lb. It is very important that you input an accurate result; Dosage — Prescribed amount of drug in mg per kg of body weight.
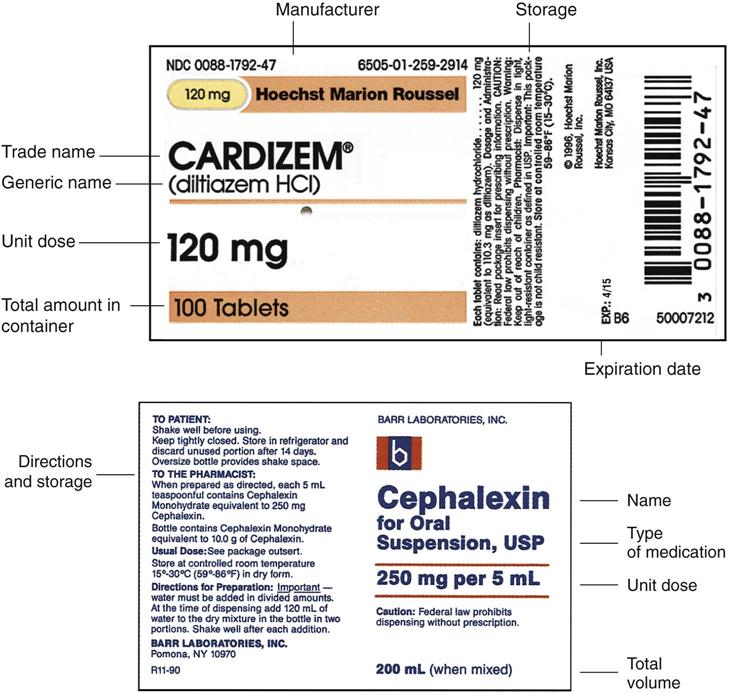
Drug Dosage Calculations | How-to-guide - KnowledgeDose The pharmacist has asked the pre-registration pharmacist to also state how many mls of colecalciferol Mr X should take on the dispensing label. What is the correct dosage on the label? Take 800 units (0.4ml) once daily Take 800 units (0.8ml) once daily Take 800 units (0.6ml) once daily Take 800 units (1ml) once daily 69 Likes About KnowledgeDose Drug Calculations: How To Use Dimensional Analysis Step 2: On the right side, place the information given with the same label needed in the numerator. In this example, we know that the drug concentration available is 0.25 mg/mL. Place mL in the numerator and 0.25 mg in the denominator. Step 3: The desired dose is 0.5 mg. Place information with the same label as the preceding denominator into ... Lecture 3: Reading Medication Labels and Basic Dosage Calculations Dosage units: mg Administration units: cap Concentration: Each capsule is 120 mg. Notice that the label just says 120 mg, but does not say whether this is the amount for a single pill or for the whole package; for packages containing pills, a single dosage like this alwaysrepresents the amount per pill. PDF Drug dosage calculation handout for BSN completion 16. The provider orders 125mg of amoxicillin Q. 8 hrs. for a patient weighing 58 lbs. Calculate the daily dosage range recommended on the label and compare the daily dose ordered by the doctor. Does the provider order fall within the usual dosage range? 17. Aggrastat is ordered to infuse at 0.1 mcg/kg/min for a patient weighing 136 lbs. A ...
LibGuides: Clinical Calculations: Module 6: Divided Doses and ... 400 mg = 1 ml (from the reconstitution directions on the label) You do not use the 1.8 ml of diluent added in your calculations, but you need this information to find the 400 mg per ml after reconstitution from the drug label. Equation for the dose in ml: Please notice: One day = 24 hours Every 8 hours = 3 doses per day Practice Problems Dosage Calculations: NCLEX-RN - Registered nursing Calculating Oral Medication Dosages Using Ratio and Proportion Here is an example of how to calculate oral medication dosage using ratio and proportion: Doctor's order: 125 mg of medication once a day Medication label: 1 tablet = 250 mg How many tablets should be administered daily? Pharmacy Dosage Calculations - Pharmacy Tech Review First, note that both grams and milligrams are used in the problem so we need to do a measurement conversion. There are 1,000 milligrams per gram. The first ratio is one dose per 20mg so ¹⁄₂₀. The second ratio contains an unknown so initially it is ˣ⁄₁₀₀₀. Set these two ratios in a proportion. Dosage Proportion With Unknown. Pharmacology Calculations and Conversions - Study.com Jan 21, 2022 · Discover the basic pharmacology conversions, identify common dosage calculations, and examine medical mathematical formulas. . Updated: 01/21/2022 ... Reading Drug Labels.
Dosage and Calculations - Registered Nurse RN Some types of dosage calculations require you to determine the dosage of a medication or the amount to be administered based on the prescribing provider's order and the patient's weight. These types of drug problems require converting pounds to kilograms and that you apply that […] Tablets and Capsules Dosage Calculations (Desired over Have Method)
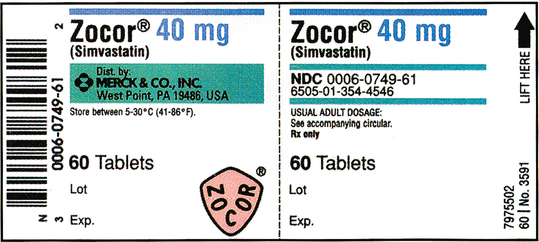
PDF Dosage Calculations Syllabus(1)new - Odessa College Chapter 6: Oral medication labels and dosage calculations (CO #1-5) The learner will: 1. Identify scored tablets, unscored tablets, and capsules. 2. Read drug labels to identify trade and generic names. 3. Locate dosage strengths and calculate average dosages. 4. Measure oral solutions using a medicine cup. Chapter 7: Safe medication administration
Dosage Calculation Reading Drug Labels - StuDocu Dosage Calculation Reading Drug Labels This tells you how to read different kinds of drug labels. University Tarleton State University Course Nursing Pharmacology (NUR 265) Academic year 2020/2021 Helpful? 1 Please or to post comments. Students also viewed Dosage Calculation Problems Elimination GI system - Lecture notes 5
Drug Calculations Involving Reading Drug Labels, Part 1 - YouTube Southwest Tech Math/Science Center 3.27K subscribers Practice performing drug dosage problems that require the use and understanding of drug labels to solve. Problem 1.) Determine the milliliters...
Dosage Calculations the Easy Way! - Straight A Nursing Everything except for tablets is crossed out, so we know we are ready to do some math. 1) Multiply across the top: 650 x 1. 2) Then divide across the bottom: ÷ 325. What answer did you get? Let's do one more easy one…. For this calculation, let's assume midazolam comes in 5 mg tablets.
Pharmaceutical Calculations 15th Edition - amazon.com Master the fundamental calculations principles and basic techniques you need to know for successful pharmacy practice! Thoroughly reviewed by practitioners, and educators, this 15th Edition maintains high standards for both academic and basic practice requirements, while offering the most comprehensive and in depth coverage of pharmacy calculations available.
Wiskundige Geletterdheid Hulpbronne / Maths Literacy Aids Length, Distance and Time; Perimeter; Area; Cost calculations ; Week 5 en 6; Buite oppervlakte en volume; Surface area and volume; Week 7; Meting - LMI en medisyne dosisse; Measurement - BMI and medicine dosage; Gr 12 - Hersiening / Revision. Kwartaal 2 hersiening ; Memorandum - Afrikaans; Term 2 revision ; Memorandum - English
PDF Medication Calculation Examination Study Guide - Los Angeles County ... Label shows 75 - 150 mg/kg per day. Is the physician's order within normal range? Solution: 6 x 75 = 450 mg (minimum dosage per day); 150 X6 = 900 (maximum dosage per day) 24 ÷ 4 = 6 dosages : 300 x 6 = 1800. Answer: Dosage is not within range. IV Calculations • [amount of fluid to be infused] x [drop factor] ÷ minutes to infuse = gtts/min
Dosage Calculation Practice_Reading Labels.pdf - Dosage... Ordered dose = 300 mg/kg/day in equal 3 doses Weight of the patient = 172 lb. Convert lb to kg 1 lb = 0.454 kg So Weight of the patient = 172 * 0.454 = 78 kg. Desired dose = 300 * 78 = 23400 mg. Dose in hand = 200 mg. Quantity = 1 ml. As per above formula ml of drug required = 23400/200 * 1 = 117 * 1 = 117 ml in 3 equal doses. So
Dosage Calculations, Dosage Calculations and Labels, Insulin and ... Dosage Calculations, Dosage Calculations and Labels, Insulin and Heparin IV Therapy, Intake and output hesinclexTeasmedsurg • Az 104 renewal exam questions and answers 2022
Nausea – Nursing Diagnosis and Care Plan - Nurseslabs 19.03.2022 · Use this nursing diagnosis guide to help you create nursing interventions for nausea nursing care plan.. Nausea is a queasy sensation that may include or not include an urge to vomit. It is a common and distressing indication with multiple causes, including chemical stimulation of the vomiting center by certain medications, chemotherapy, intracranial lesions, ingestion of …
Hypothermia – Nursing Diagnosis & Care Plan - Nurseslabs 19.03.2022 · Use this guide to create a nursing care plan and nursing interventions for hypothermia.. Normal body temperature is around 37 °C (98.6 °F). Hypothermia occurs as the body temperature falls lower than normal; usually below 35 °C (95 °F). Hypothermia occurs when the body fails to produce heat during metabolic processes, in cells that support vital body …
Dosage Calculations, 9th edition 9th Edition - amazon.com Dosage Calculations, 9th edition: 9781439058473: Medicine & Health Science Books @ Amazon.com Skip to main content ... Featuring full-color images of drug labels, critical thinking assessments, extensive clinical examples, and a host of interactive supplements, including an accompanying online tutorial, DOSAGE CALCULATIONS, 9th Edition provides the skills needed …
Nursing Pharmacology: Dosage And Calculations Practice Test - RN speak Dosage and Calculations Practice Test 1. The nurse is administering mannitol to the client with a head injury. The order reads 1,000 mL IVPB over 6 hours. At which rate should the nurse administer the medication via a pump? Answer: _______ mL per hour. 2. The client diagnosed with bacterial endocarditis is prescribed gentamicin IV piggyback (IVPB).
PDF Formulas for Calculating Medication Dosage - Indian Hills Community College Dosage Calculations This unit looks at drug calculations. It's important to remember any time we do calculations we must ... the medication label, and Q (quantity) is the volume in which the dosage strength is available (e.g. tablets, capsules, milliliters). For example: we have an order for Ceclor 0.5 g PO b.i.d. We have available 250 mg ...
Dosage Calculation - Label Reading | Other - Quizizz Quiz Dosage Calculation - Label Reading Played 414 times Other, Life Skills 6 months ago by shelley_dinkens_86955 3 Save Edit Live modes Start a live quiz Asynchronous learning Assign homework 10 questions Preview Show answers Question 1 30 seconds Q. What is the dosage strength? answer choices 150 325 650 Not listed Question 2 30 seconds Q.
Delmar Cengage Learning Companions - Math for Meds, Dosages and Solutions Chapter 9: Parenteral Medication Labels and Dosage Calculation / 104; Chapter 10: Reconstitution of Powdered Drugs / 126; Chapter 11: Measuring Insulin Dosages / 142; SECTION 4: DOSAGE CALCULATIONS; Chapter 12: Ratio and Proportion / 164; Chapter 13: Dimensional Analysis / Units Conversion / 196;
5 Peptic Ulcer Disease Nursing Care Plans - Nurseslabs Mar 18, 2022 · The nursing goals of a client with a peptic ulcer disease include reducing or eliminating contributing factors, promoting comfort measures, promoting optimal nutrition, decreasing anxiety with increased knowledge of disease, management, and prevention of ulcer recurrence and preventing complications. Here are five (5) nursing care plans (NCP) for peptic ulcer disease:
Pharmacy Dosage Calculations | Pharmacy Math Made Simple! - PharmaFactz 0.5mg x 1,000 = 500 micrograms. Adrenaline is available as an injection of 100 micrograms/mL. Therefore we need 5mLof the available adrenaline formulation. Answer: 5mL Sample Problem 5 The recommended dose of fluconazole for mucosal candidiasis in children is 3mg/kg daily. Calculate the dose needed for a child (3-years old).
Dosage and Calculations Math Practice - StuDocu Any of the following thr ee methods can be used to perform drug calculations. Pl ease. re view all thre e methods and select the one that works for you. It is important to ... H = dose on container label or d ose on hand . V = form and amou nt in which drug comes (tablet, capsule, liquid) Example: Order-Dilantin 50 mg po TID.
Drug Calculations Practice NCLEX Questions (100+ Items) - Nurseslabs Methods for Drug Dosage Calculations Standard Method The commonly used formula for calculating drug dosages. Where in: D = Desired dose or dose ordered by the primary care provider. H = dose on hand or dose on the label of bottle, vial, ampule. V = vehicle or the form in which the drug comes (i.e., tablet or liquid). STANDARD FORMULA
Dosage Calculation Resources - Calhoun Community College Session 4 Medication Labels Session 5 Formula Method and Ratio to Proportion.pptx Session 6 Parenteral Dosage Session 7 Reconstitution of Solutions & Enteral Feedings Session 8 Pediatric Problems Session 9 IV Calculations Practice Problems Calculating using Labels with Answers Practice Problems Part 1 with Answers
















![Drug Calculations Online for Calculate with Confidence [Access Code] by Morris R 9780323056380 | eBay](https://i.ebayimg.com/images/g/NvYAAOSw1w1hXrKq/s-l500.jpg)

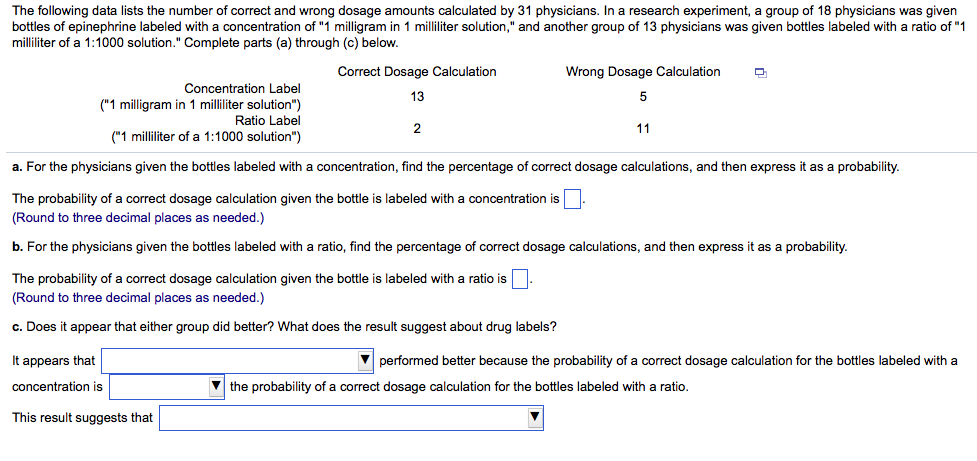




Post a Comment for "43 dosage calculations with labels"